NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
A SUMMER TRAINING REPORT
Submitted by
Abhijeet Katiyar
1684000002
In partial fulfillment of industrial training for the award of the degree of
BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY
IN
CIVIL ENGINEERING

Rajkiya Engineering College, Mainpuri
RECM
NH84 Road Nauner, Bhongoan – Mainpuri – Shikohabad Road, Mainpuri
Uttar Pradesh 205001
July 2018
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I would like to place on record my deep sense of gratitude to Er. P. P. Verma, line civil engineering for his generous guidance, help and useful suggestions.
I express my sincere gratitude to Er. P. P. Verma for his stimulating guidance and continuous encouragement.
I also wish to extend my thanks to Mr. Praveen Katiyar and other workers for guiding and providing the knowledge related to machinery and processes.
I am extremely thankful to my faculty, REC Mainpuri and training placement cell REC Mainpuri for valuable suggestions and encouragement.
SIGNATURE OF STUDENT
ABSTRACT
As a part of curriculum, and for the partial fulfilment of the requirements for completion of Bachelor of technology degree from Rajkiya Engineering College, Mainpuri.
The report consists of brief study and description of materials, equipments and procedures used at the site for construction.
Every student who has passed 117 credit hours or more can take this 3 hours credit course; the period of the training is 40 days.
The purpose of this course is to apply the theoretical knowledge into practical work.
There was two main parts in our training, the first part was practical part and the second part is office work.
The student can be trained as site engineer; it’s give you the opportunity to supervise the construction work closely and properly, or as design engineer using software programs such as STAAD PRO, AUTOCAD etc.
The training started at and last till during this you can see the subsequent of the construction work and how to manage and control the work due to schedule.
In this report, I try to explain my 4 weeks experience in the PWD, Bareilly. The content of all chapters is broadly explained and it is constructed from the practical basis of the site works.
Table of Contents
| S. No. | Contents | Page no. |
| 1. | Title Page | 1 |
| 2. | Certificate by Supervisor | 2 |
| 3. | Acknowledgement | 3 |
| 4. | List of Photographs | 4 |
| 5. | Abstract | 5 |
Chapter 1
| S. No. | Contents | Page No. |
| 1. | PWD: An Overview | 5 |
| 2. | Introduction | 5-11 |
| 3. | Road Construction | 12-13 |
| 4. | Soil | 14 |
| 5. | Aggregate | 14 |
| 6. | Portland Cement and Concrete | 14 |
| 7. | Testing Methods on Highway Materials | 15-17 |
Chapter 2
| S. No. | Contents | Page No. |
| 1. | Bitumen Road Construction | 18 |
| 2. | Application of Tuck Coat | 18 |
| 3. | Preparation and Placing of Premix | 18 |
| 4. | Rolling | 18-19 |
| 5. | Finished Surface | 20 |
| 6. | Highway Drainage | 20 |
| 7. | Highway machinery | 21-22 |
| 8. | Conclusion | 22 |
List of photographs
| S. No. | Name of Photo |
| 1.0 | National Highway |
| 1.1 | State Highway |
| 1.2 | District Road |
| 1.3 | Rural Road |
| 1.4 | Earthen Road |
| 1.5 | Gravel Road |
| 1.6 | Murrum Road |
| 1.7 | Kankar Road |
| 1.8 | WBM Road |
| 1.9 | Bituminous Road |
| 1.10 | Concrete Road |
| 1.12 | Parts of Road |
| 1.13 | Crushing Test |
| 1.14 | Abrasion Test |
| 2.1 | Rolling |
| 2.2 | Quality Control |
| 2.3 | Highway Drainage |
| 2.4 | Motor Grader |
| 2.5 | Asphalt Mixing Plant |
| 2.6 | Road Roller Machine |
| 2.7 | Crawler Excavator |
| 2.8 | Wheel Loader |
CHAPTER 1
Public Work Department(PWD): An Overview
Public work department, under the Ministry of public work department, is the pioneer in construction arena of Uttar Pradesh. Over about four centuries, PWD could successfully set the trend and standard in the states infrastructures development. It plays a pivotal role in the implementation of government construction projects. It also undertakes projects for autonomous bodies as deposit works. Public Work Department has highly qualified and experienced professionals forming a multi-disciplinary team of civil, electrical and mechanical engineers who work alongside architects from the Department of Architecture.
With its strong base of standard and professionalism developed over the years, PWD is the repository of expertise and hence the first choices among discerning clients for any type of construction project in Uttar Pradesh. Besides being the construction agency of the government, it performs regulatory function in setting the pace and managing projects for the country’s construction industry under the close supervision of the Ministry of Housing and Public Works.
The Public Work Department has highly qualified and experienced professionals forming a multi-disciplinary team of civil, electrical and mechanical engineers who work alongside architects from the Department of Architecture. As a sister organization falling under the administrative control of the nation. With its strong base of standards and professionalism developed over the years, the PWD is the repository of expertise and hence the first choices among discerning clients for any type of construction project. It is recognised as a leader and pacesetter in the construction industry because of its consistently superior performance.
INTRODUCTION
The Department of a country depends on the connectivity of various places with adequate road networks. Roads are the major channel of transportation for carrying goods and passengers. They play a significant role in improving the socio-economic standards of a region. Roads constitute the most important mode of communication in areas where railways have not developed much and from the basic infrastructure for the development and economic growth of the country.
The benefits from the investment in the road sector are indirect, long-term, and not immediately visible. Roads are important assets for any nation. However, merely creating these assets is not enough, it has to be planned carefully and a pavement that is not designed properly deteriorates fast. India is a large country having huge resources for materials.
If these local materials are used properly, the cost of construction can be reduced. These are various type of pavement which differ in the suitability in different environments. Each type of pavement has its own merits and demerits. Despite a large number of seminars and conferences, still in India, 98% of roads are having flexible pavements. A lot of research has been made on the use of Waste Materials but the role of these materials is still limited. So, there is a need to take a holistic approach and mark the areas where these are most suitable.
India has one of the largest road networks in the world (over 3 million km at present). For the purpose of management and administration, roads in India are divided into the five categories which are on the next page:
- NATIONAL HIGHWAY (NH)
- STATE HIGHWAYS (SH)
- MAJOR DISTRICT ROADS (MDR)
- OTHER DISTRICT ROADS (ODR)
- VILLAGE ROADS (VR)
The National Highway is intended to facilitate medium and long-distance intercity passenger and freight traffic across the country. The state highways are supposed to carry the traffic along with the major centers within the state. Other District Roads and Village Roads provide villages accessibility to meet their social needs as also the means to transport agriculture produce from village to nearby markets. Major District Roads provide the secondary function of linkage between main roads and rural roads.
The successful operation of various schemes for the Public Work Department engineers and supervisory boards in different districts of the engineer’s office has been settled. Activities by planning, execution, and quality control, etc. remove impediments find joy in relation to the supervision over the activities are focused. Various schemes operated by the Department of the Office of the Regional Chief Engineers and Chief Engineers Office.

National Highway (1.0)
NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
There are some types of road which is based on materials-
- Earthen Roads
- Gravel Roads
- Murrum Roads
- Kankar Roads
- WBM Roads (Water Bound Macadam)
- Bituminous Roads
- Concrete Roads



Road Construction
There are mainly 4 basic layers in roads which are defined below-
Sub-Grade
The sub-grade material should be clean and free from organic matter and should be able to be compacted by roller, to form stable sub-base.
The material should have the following characteristics:
- Well graded, uniformity coefficient (D60/D10) should be less than 3.
- Fraction passing sieve#200 shall not be greater than 2/3rd of the fraction passing sieve#40.
- Should have a L.L not greater than 25%.
- P.I not greater than 6.
- In coarse grain, aggregate retained by #10 sieve, percentage of wear not be greater than 5%.
- The maximum dia. of any particle shall not be greater than 2/3rd of the layer thickness of the sub-base.
Typical particle size distribution for the sub-base which will meet strength requirements are:
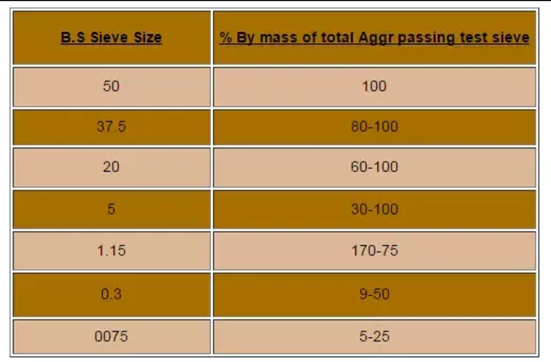
NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
Sub-base Course
- It is a layer of granular material provided above sub-grade generally natural gravel. It is usually not provided on sub-grade of good quality.
- The materials used may be either unbound granular, or cement-bound. The quality of sub-base is very important for the useful life of the road and can outlive the life of the surface, which can be scrapped off and after checking that the sub-base is still in good condition, a new layer can be applied.
Base Course
- It is the layer immediately under the wearing surface (Applied whether the wearing surface is bituminous or cement concrete and whether it’s a thick or thin bituminous layer).
- As base course lies close under the pavements surface it is subjected to severe loading. The material in a base course must be of extremely high quality and its construction must be done carefully. The LA Abrasion test can determine the quality of the aggregate for this purpose.
Type of base-course
- Granular Base course
- Macadam Base course
- In-water bound Macadam
- Treated Bases
Surface Course
The top layers of pavement which are in direct contact with the wheel of the vehicle. Usually constructed of material in which bitumen is used as binder materials.
National Highway 730
Soils
Major works of man since the beginning of time have depended on the use of soils.
- Not only does soil form the foundation, or supporting surface for buildings, bridges, roadways, and culverts, but it is the most common constituent, in the form of aggregate.
- Soils are the most basic abundant material in highway engineering and as such, are well characterized by the expression “common as dirt”.
- The steps are taken to prepare foundations to manipulate and transport soils and prepare them for use as aggregates account for well over 70% of the total cost of construction for a normal highway project.
Aggregates
- The surface, base, and sub-base of pavements consist of aggregates or a mixture of aggregates with cement and water (Portland cement) or a bituminous material (bituminous concrete).
- The strength properties of a layer are a function of both the quality and the properties of ingredients.
- Aggregates are hard, durable, mineral materials obtained by mining or quarrying operations of deposits of sand, gravel, talus or ledges and may be defined as “granular material of mineral composition”.
Portland Cement Concrete
- Portland cement is a mixture of Portland cement, water, air, sand, and gravel or crushed stone.
- It is formed when the cement and water combine chemically and binds the entire mixture into a rock-like mass.
- It may be thought of as a two-component material; paste and aggregate.
- The paste is comprised of cement, water, and entrained air.
- The aggregate portion is generally composed of sand and gravel and comprises 70 to 80 % of the volume of the concrete.
- Aggregate both fine and course should be selected for their quality, strength, durability, and resistance to environmental effects.
NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
TESTING METHODS ON HIGHWAY MATERIALS
- Moisture Condition Value (MCV) Test
- California Bearing Ratio (CBR) Test
- Dynamic Cone Penetrometer
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
- Penetration Test on Bitumen
- Softening Point Test on Bitumen
- Los Angles Abrasion Value Test
- Flakiness Index Test
CBR Test for Sub-grade
- The California Bearing Ratio (CBR) is a penetration test for evaluation of the mechanical strength of natural ground, subgrades and basecourses beneath new carriageway construction.
- Subgrade soil is the integral part of the road pavement structure which provides support of the pavement. The subgrade and its different properties are very much important in the pavement design structure.
- The major function of the subgrade is to provide the support to the pavement against traffic loading and for this subgrade should possess sufficient stability under adverse climate and heavy loading conditions.
- The strength of a soil or subgrade can be determined by using a test known as CBR Test which was developed in California in the year 1930’s and it is way to determine the standard soil properties such as density.
CBR= (TEST LOAD / STANDARD LOAD) *100
The following table gives the standard loads adopted for different penetrations for the standard material with CBR value of 100%-
| PENETRATION OF PLUNGER (mm) | STANDARD LOAD (kg) |
| 2.5 | 1370 |
| 5.0 | 2055 |
| 7.5 | 2630 |
| 10.0 | 3180 |
| 12.5 | 3600 |
NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
TEST ON AGGREGATES
Aggregate plays an important role in pavement construction. Aggregates influence, to a great extent, the load transfer capability of pavements, following tests are carried out-
- Crushing Test
- Abrasion Test
- Impact Test
- Soundness Test
- Specific Gravity and Water Absorption Test
- Bitumen Adhesion Test
CRUSHING TEST
Crushing test is used to determine the crushing strength of aggregates. The aggregate crushing value provides a relative measure of resistance of crushing under gradually applied crushing load.

ABRASION TEST
Abrasion test is carried out to test the hardness property of aggregates and to decide whether they are suitable for different pavement construction works. Los Angles Abrasion test is a preferred one for carrying out the hardness property and has been standardized in INDIA.

SOUNDNESS TEST
Soundness test is intended to study the resistance of aggregates to weathering action, by conducting accelerated weathering test cycles. The Porous aggregates subjected to freezing and thawing is likely to disintegrate prematurely. To ascertain the durability of such aggregates, they are subjected to an accelerated soundness test.
The loss in weight should not exceed 12% when tested with Sodium Sulphate and 18% with Magnesium Sulphate solution.
NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
TESTS ON BITUMEN
- Penetration Test
- Ductility Test
- Softening Test
- Specific Gravity Test
- Viscosity Test
- Flash and Fire Point Test
- Float Test
- Water Content Test
- Loss on Heating Test
CHAPTER 2
BITUMEN ROAD CONSTRUCTION-
The primary use (70%) of Asphalt/Bitumen is in road construction, where it is used as the glue or binder mixed with aggregate particles to create asphalt concrete.
Preparation of the existing base course layer
- The existing surface is prepared by removing the pot holes or rust if any. The irregularities are filled in with premix chippings at least a week before laying surface course.
- If the existing pavement is extremely way, a bituminous levelling course of adequate thickness is provided to lay a bituminous concrete surface course on a binder course instead of directly laying it on a WBM.
Application of tuck coat
It is desirable to lay the AC layer over a bituminous base or binder course. A tuck coat of bitumen is applied at 6 to 7.5 kg per 10 square meter area, this quantity may be increased to 7.5 to 10 kg for a non-bituminous base.
Preparation and Placing of Premix
- The premix is prepared in a hot mix plant of a required capacity with the desired quality control. The bitumen may be heated up to 150 to 177 deg. C and the aggregate temperature should not differ by over 14 deg. C from the binder temperature.
- The hot mixed material is collected from the mixture by the transporters, carried to the location is spread by a mechanical paver at a temperature of 121 to 163 deg. C.
- The camber and the thickness of the layer are accurately verified.
- The control of the temperatures during the mixing and the compaction are of great significance in the strength of the resulting pavement structure.
Rolling
- A mix after it placed on the base course is thoroughly compacted by rolling at a speed not more than 5 km per hour.
- The initial or break down rolling is done by 8 to 12 tonnes roller and the intermediate rolling is done with a fixed wheel pneumatic roller of 15 to 30 tonnes having a tyre pressure of 7 kg per square cm the wheels of the roller are kept damp with water.
- The number of passes required depends on the thickness of the layer. In warm weather rolling on the next day, helps to increase the density if the initial rolling was not adequate. The final rolling or finishing is done by 8 to 10 tonne tandem roller.

NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
Quality control of bituminous concrete construction
- The routine checks are carried out at site to ensure the quality of the resulting pavement mixture and the pavement surface.
- Periodical checks are made for,
- Aggregate grading
- Grade of bitumen
- Temperature of aggregate
- Temperature of paving mix during mixing and compaction.

Finished Surface
The AC surface should be checked by a 3.0 m straight edge. The longitudinal undulations should not exceed 8.0 mm and the number of undulations higher than 6.0 mm should not exceed 10 in a length of 300 mm. The cross-traffic profile should not have undulations exceeding 4.0 mm.
Highway Drainage
- Its purpose is to drain rain water from the highway into the sewerage system. A highway drain is the pipe connecting the highway gully to the surface water sewer.
- A soakaway is a drainage pit covered by a metal cover or sometimes by soil. Its purpose is to allow rain water from buildings to permeate into the surrounding subsoil. These are sometimes used to drain the highway.
- Highway drainage should prevent flooding, ponding and seepage and keep the carriageway, cycleway and footway as free of standing water as possible.
- It ensures surface water falling on the highway enters the drainage system or natural watercourse as speedily as possible.
- Keep the underlying road structure as dry as possible.
- Prevent injury or damage caused by hazardous surface water.
- Prevent highway surface water flooding adjacent properties.
- Prevent blockages in associated highway drainage system with consequential flooding.

NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
Highway Machineries





Summary of initial and life cycle cost (Rs. LAKH)
| S.No. | Pavement Type | Initial Cost | Life cycle construction/ Maintenance Cost | |
| 1. | Flexible/Bituminous | 21 | 33.60 | |
| 2. | Rigid/Concrete | 27 | 28.30 | |
| 3. | Rigid/Concrete with 30% Fly ash replacement | 25.25 | 26.50 |
NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
Conclusion
India’s economic growth plan of over 6% per annum for the next 20 years will, to a great extent, depend on an efficient road infrastructure, not only national highways but other roads too, including link roads for rural connectivity, which can provide fast movement of goods and people with safety and economical cost to the user, government of India has drawn up Pradhan Mantri gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) for implementation of rural connectivity. It is estimated that in the next few years, road works under PMGSY worth Rs. 1,20,000 Crores are to be constructed.
Since road pavements are an important part of these projects, costing about 50% of the investment, a careful evaluation of the alternatives is necessary to make the right choice on a rational basis, which may be comparatively more beneficial to the nation.
Feel free to ask for word file of – NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730
Right Understanding
Right Understanding We all know that the Human Desire is to be in continuous happiness which is the need of I (self). But do you know, from where Continuous happiness will come? No, right! So continuous happiness is to be in Right Understanding, Right Feeling, and Right Thought that is Activity of I (Self). Do…
Where We Are
Where We Are (Self-Evolution) We exist as human being. We want to live a fulfilling life. We have some desires and we have some programs for the fulfilment of it. We need to understand our basic aspiration and program for its fulfillment correctly and comprehensively. Only then, we can ensure fulfillment. We should explore ourselves…
Highway Construction
Highway Construction Embankment Construction Materials and General Requirements The materials used in embankments, subgrades, earthen, shoulders, and miscellaneous backfills shall be soil, moorum, gravel, a mixture of these. Clay having liquid limit exceeding 70 and plasticity index exceeding 45; shall be considered unsuitable for embankment. Sub-grade and top 500mm portion of the embankment just below…
Special Concretes
Special Concretes Concrete is most vital material in modern construction. In addition to normal concrete, other varieties in use are, high strength and high-performance concrete, self-compacting, lightweight, high density, fiber reinforced, polymer, colored concrete, etc. The making of concrete is an art as well as a science. Special types of concrete are those with out-of-the-ordinary…
Marketing Practices
Marketing Practices Success in the world of business, no matter how you earn it, you have to rule on the marketplace. Although luck plays a role in the outcome of the market strategies. In the business decisions, there should be the understanding of market otherwise the failure will take place by the marked decisions. While…
Risk Analysis
Risk Analysis The risk that remains after the implementation of controls is called the residual risk. All systems will have residual risk because it is virtually impossible to completely eliminate risk to an IT system. In other words, we can say that there are two main parts of the security risk analysis known as Quantitative…
NATIONAL HIGHWAY 730









Recent Comments